CPLharbour
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - CPL/Closed Polygon Lists
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.5, Creation date: 2019-02-28, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns the inner contour of an area limited by line type areas
See Also: CPLconvexhull
, CPLconvexhulldelaunay
, delaunayofCPL
, CPLfillin
, CPLfillinside
, CPLfillgap
Example Illustration
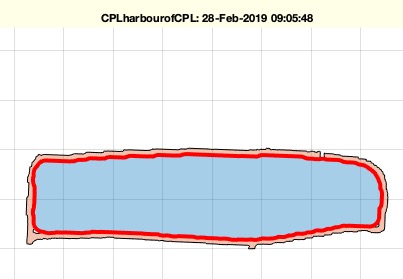
Syntax
[CPLN,ps]=CPLharbour(CPL,[inside,d])
Input Parameter
CPL: | | CPL or Polyshape |
inside: | | true = inside; false = outside area |
d: | | distance to bridge |
Output Parameter
Examples
CPLharbour(CPLsample(29));
CPLharbour(CPLsample(29),false);
CPLharbour(CPLsample(29),false,0);
CPLharbour(CPLsample(18),false,-1);
Copyright 2019-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, CPLharbour, is designed to return the inner contour of an area defined by line-type areas. It is part of the SolidGeometry library and was introduced in version 4.5.
Input Parameters
- CPL: This can be a Closed Polygon List (CPL) or a Polyshape object.
- inside: A boolean parameter where
true indicates the area inside the contour, and false indicates the area outside. The default value is true.
- d: A numeric value representing the distance to bridge. If not provided, it is calculated based on the bounding box of the convex hull.
Output Results
- CPLN: The vertices of the resulting contour.
- ps: A polyshape object representing the processed shape.
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve the
inside and d parameters using getfuncparams, with default values true and [] respectively.
- Convert
CPL to a polyshape if it is numeric, with simplification turned off.
- Compute the convex hull of the polyshape using
convhull.
- If
d is not provided, calculate it as one-eightieth of the bounding box size of the convex hull.
- Create a buffer around the polyshape and subtract it from the convex hull, then buffer the result again.
- If the resulting shape has no regions, revert to the original polyshape.
- Intersect the buffered shape with the convex hull.
- If
inside is false, union the buffered shape with the original polyshape.
- Sort the regions of the resulting shape by area in descending order.
- Extract the vertices of the largest region as
CPLN.
- If no output is requested, plot the results using
SGfigure, CPSplot, and CPLplot.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:44. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21