CPLofPL
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Auxiliary function
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 2.0, Creation date: 2014-12-06, Last change: 2025-09-14
appends the first point to a point list of required
Description
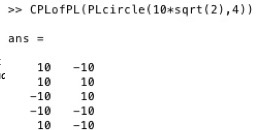
The last point of a CPL has to be the first point.
Slow, please try to avoid if possibile
See Also: PLofCPL
, CPLofPLcontour
Example Illustration
Syntax
CPL=CPLofPL(PL)
Input Parameter
Output Parameter
Copyright 2014-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, CPLofPL, is designed to convert a point list (PL) into a closed polygon list (CPL). The function ensures that the last point of the CPL is the same as the first point, effectively closing the polygon.
Input Parameters
- PL: A point list, which can be a matrix or a cell array of matrices. Each matrix represents a list of points in 2D space.
Output Results
- CPL: A closed polygon list, which is a matrix where the last point is the same as the first point.
Algorithm Steps
- Check if the input
PL is empty. If it is, return an empty CPL.
- Initialize
CPL with PL.
- If
PL is a cell array, iterate over each element:
- For the first element, recursively call
CPLofPL and assign the result to CPL.
- For subsequent elements, append
NaN NaN and the result of the recursive call to CPL.
- If
PL is not a cell array:
- Check if
PL contains NaN values. If it does, assign PL to CPL.
- If the last point is not equal to the first point, append the first point to
PL to form CPL.
- Use the function
separateNaN to determine the number of separate polygons in CPL.
- For each separate polygon:
- Extract the polygon using
separateNaN.
- If the first point is not equal to the last point, or if the polygon has only one point, append the first point to close the polygon.
- Use
replaceNaN to update CPL with the closed polygon.
- If no output is requested, plot the original and closed polygons using
SGfigure, VLplot, and CPLplot.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 08:27. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21