CPLpinholesinCPL
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - CPL/Closed Polygon Lists
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.7, Creation date: 2019-07-06, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns the CPLs of the pins that would fit into bore holes of servos or PCB
Description
.. on the flight JHU, Baltimore..
support real holes or structures at the outer
See Also: CPLofSGboreholes
, CPLofSGhull
Example Illustration
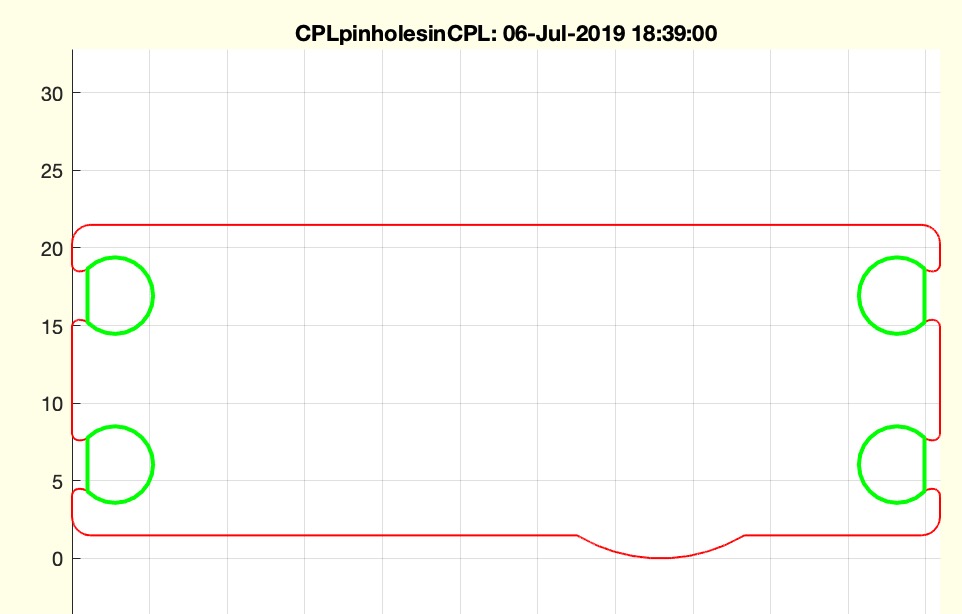
Syntax
CPLH=CPLpinholesinCPL(CPL,[rmin,bord])
Input Parameter
CPL: | | CPL created by CPLofSGboreholes |
rmin: | | minimal radius to consider; default 2 mm |
bord: | | border of the outer contour that should not be touched by the pins; default 1mm |
Output Parameter
CPLH: | | CPL of pins that fit into the bore holes |
Examples
SGcmdsample('3156'); C=ans;
CPLofSGboreholes(C,'',1.5); CPLC=ans; CPLplot(CPLC,'m',4);
CPLpinholesinCPL(CPLC,1);CPLH=ans;
bb=BBofSG(C), SGofCPLz(CPLH,bb([5:6])), SGplotalpha(C,'r',0.2);
Copyright 2019-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, CPLpinholesinCPL, is designed to determine the CPLs (Closed Polygonal Lines) of pins that can fit into bore holes of servos or PCBs. It is part of the SolidGeometry library.
Input Parameters
- CPL: A CPL created by the function
CPLofSGboreholes.
- rmin: The minimal radius to consider for the holes. The default value is 2 mm.
- bord: The border distance from the outer contour that should not be touched by the pins. The default value is 1 mm.
Output
- CPLH: The CPL of pins that fit into the bore holes.
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve the minimal radius
rmin and border bord from the input parameters or use default values if not provided.
- Calculate
Amin, the minimum area for a hole, using the formula: Amin = rmin * rmin * pi * 0.8.
- Compute the convex hull of the input
CPL and buffer it by -bord to create a new CPL.
- Perform a boolean subtraction between the buffered convex hull and the original
CPL to get CPLH.
- Calculate the area of each component in
CPLH and store it in a.
- Identify indices
ii where the area is greater than or equal to Amin.
- If there are valid indices, select the corresponding components from
CPLH; otherwise, set CPLH to an empty array.
- If no output is requested, plot the original
CPL in red and the resulting CPLH in green.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:58. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21