CPLselectbyP
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - CPL/Closed Polygon Lists
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.0, Creation date: 2020-10-04, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns an index list to select enclosing CPLs
Description
should be renamed to CPLselectbyenclosedP in future
See Also: crosstest
, insideCPL
, insideCPS
, isInteriorofCPL
, CPLselectbynearestP
Example Illustration
Syntax
ind=CPLselectbyP(CPL,PL);
Input Parameter
CPL: | | CPL |
PL: | | Single point to check |
Output Parameter
Examples
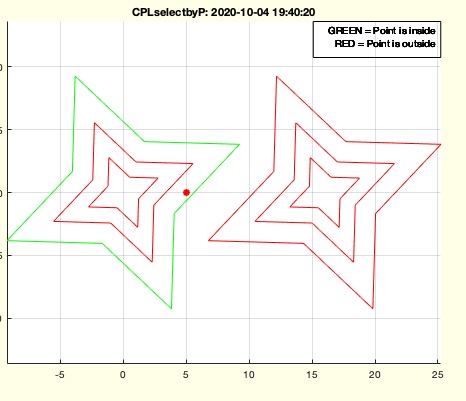
CPLselectbyP(CPLsample(14),[0 0 0])
CPLselectbyP(CPLsample(14),[5 0 0])
CPLselectbyP(CPLsample(14),[5 0 ;10 -3])
Copyright 2020-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, CPLselectbyP, is designed to determine which closed polygons (CPLs) from a list enclose a given set of points (PL). It returns an index list indicating which polygons enclose the points.
Input Parameters
- CPL: A list of closed polygons. Each polygon is defined by a series of points, and polygons are separated by NaN values.
- PL: A list of points to check against the polygons. Each point is represented as a row vector.
Output
- ind: An index list where each entry corresponds to a polygon. A non-zero value indicates that the polygon encloses at least one of the points in PL.
Algorithm Steps
- Use
separateNaN to determine the number of polygons (n) and their boundaries (b) within the CPL list.
- Initialize an index list
ind with zeros, having a length equal to the number of polygons.
- Iterate over each point in PL:
- For each point, iterate over each polygon:
- Extract the current polygon
CPLi using the boundaries from b.
- Check if the point is inside the polygon using
isInteriorofCPL.
- If the point is inside, set the corresponding index in
ind to the point's index.
- If no output is requested (nargout == 0), visualize the results:
- Plot each polygon, using green if it encloses a point and red otherwise.
- Plot the points in PL as red stars.
- Add a plot annotation to explain the color coding.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 01:38. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21