CVLclipT
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - CVL/Closed Vertex Lists
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.1, Creation date: 2017-08-22, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns a clipped CVL relative to a HT matrix
Description
Be careful if more than one axis is clipped! unexpected results .....
See Also: CVLinsertT
Example Illustration
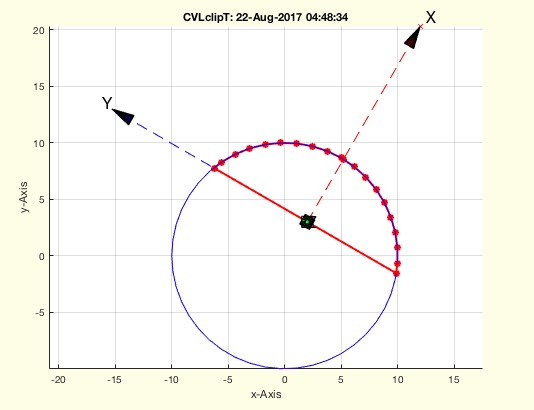
Syntax
CVLC=CVLclipT(CVL,T,ax)
Input Parameter
CVL: | | Closed Polyggon in 3D |
T: | | Frame matrix |
ax: | | clipping area; [1 0 0]; [-1 0 0]; [0 1 0]; [0 -1 0] |
Output Parameter
Examples
CVLclipT(VLaddz(PLcircle(10)),TofR(rot(0,0,pi/3),[2 3 0]),[0 0 0])
CVLclipT(VLaddz(PLcircle(10)),TofR(rot(0,0,pi/3),[2 3 0]),[-1 0 0])
CVLclipT(VLaddz(PLcircle(10)),TofR(rot(0,0,pi/3),[2 3 0]),[0 1 0])
Copyright 2017-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, CVLclipT, is designed to clip a closed polygon in 3D space relative to a given transformation matrix. The function is part of the SolidGeometry library and was introduced in version 4.1.
Input Parameters
- CVL: A closed polygon in 3D space.
- T: A transformation matrix, typically a homogeneous transformation matrix (HT matrix).
- ax: A vector indicating the clipping area. Possible values include [1 0 0], [-1 0 0], [0 1 0], [0 -1 0], which correspond to different axes and directions for clipping.
Output
- CVLC: The clipped contour of the polygon.
Algorithm Steps
- Transform the input polygon
CVL using the transformation matrix T by calling CVLinsertT.
- Apply an inverse transformation to the polygon using
VLtransT with the inverse of T.
- Round the transformed coordinates using
rounddiv to handle numerical precision issues.
- Clip the polygon based on the
ax vector:
- If
ax(1) > 0, retain points where the x-coordinate is non-negative.
- If
ax(1) < 0, retain points where the x-coordinate is non-positive.
- If
ax(2) > 0, retain points where the y-coordinate is non-negative.
- If
ax(2) < 0, retain points where the y-coordinate is non-positive.
- If
ax(3) > 0, retain points where the z-coordinate is non-negative.
- If
ax(3) < 0, retain points where the z-coordinate is non-positive.
- Transform the clipped polygon back using
VLtransT with the original transformation matrix T.
- Remove successive identical points using
VLremsuccident and convert the vertex list back to a closed polygon using CVLofVL.
- If no output is requested, plot the original and clipped polygons using
SGfigure, tplot, and CVLplot.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 06:58. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21