PCfindplanes
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Experiments
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.3, Creation date: 2018-09-26, Last change: 2025-08-19
EXPERIMENT TO SHOW THE PLANES IN AN IMAGE
See Also: PCofVL
, PCplot
Example Illustration
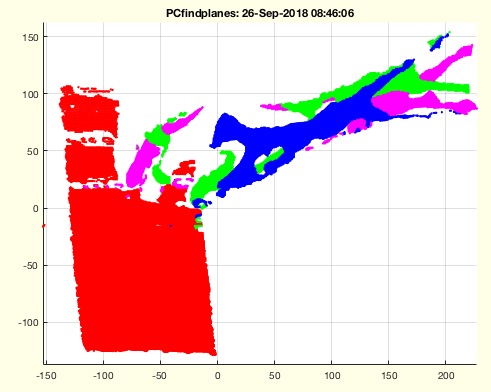
Syntax
PCfindplanes(PC)
Input Parameter
Copyright 2018-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This algorithm is designed to find planes within a point cloud and visualize them. It is part of the SolidGeometry library and was introduced in version 4.3. The function is experimental and not ready for final release as of the last update.
Input Parameters
- PC: The primary input, which is a point cloud. If the input has three columns, it is converted into a pointCloud object.
- varargin: Optional parameters that can be passed to the function. The first optional parameter can specify the depth of the planes to be searched.
Algorithm Steps
- Check if the input PC has three columns. If so, convert it to a pointCloud object.
- Calculate the bounding box of the point cloud using the function
sofBB and determine the depth of the planes to be searched, defaulting to 1% of the bounding box depth.
- Print the depth of the planes being searched.
- Initialize a figure for visualization using
SGfigure.
- Initialize arrays
NL and VLC to store normal vectors and locations of planes found.
- Set a loop to iterate up to 9 times to find planes within the point cloud.
- In each iteration, perform the following:
- Increment the counter
k.
- Determine the color for plotting using
colofn.
- Use
pcfitplane to fit a plane to the point cloud with a specified depth and maximum angular distance of 5 degrees.
- Store the locations of the points belonging to the plane in
VLc.
- Plot the plane using
VLplot and adjust the plot's lighting.
- Update the point cloud to exclude the points that belong to the found plane.
- After the loop, calculate the difference in angles between the normal vectors of the planes found.
- Filter the planes based on the angle difference to identify those that are nearly perpendicular.
- Visualize the final set of planes that meet the angle criteria.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:05. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21