SGdragchain
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Parametric Design
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.2, Creation date: 2022-05-13, Last change: 2025-08-18
creates a 3D printable already assembled drag chain
See Also: SGdragstrip
, SGdragchainelement
Example Illustration
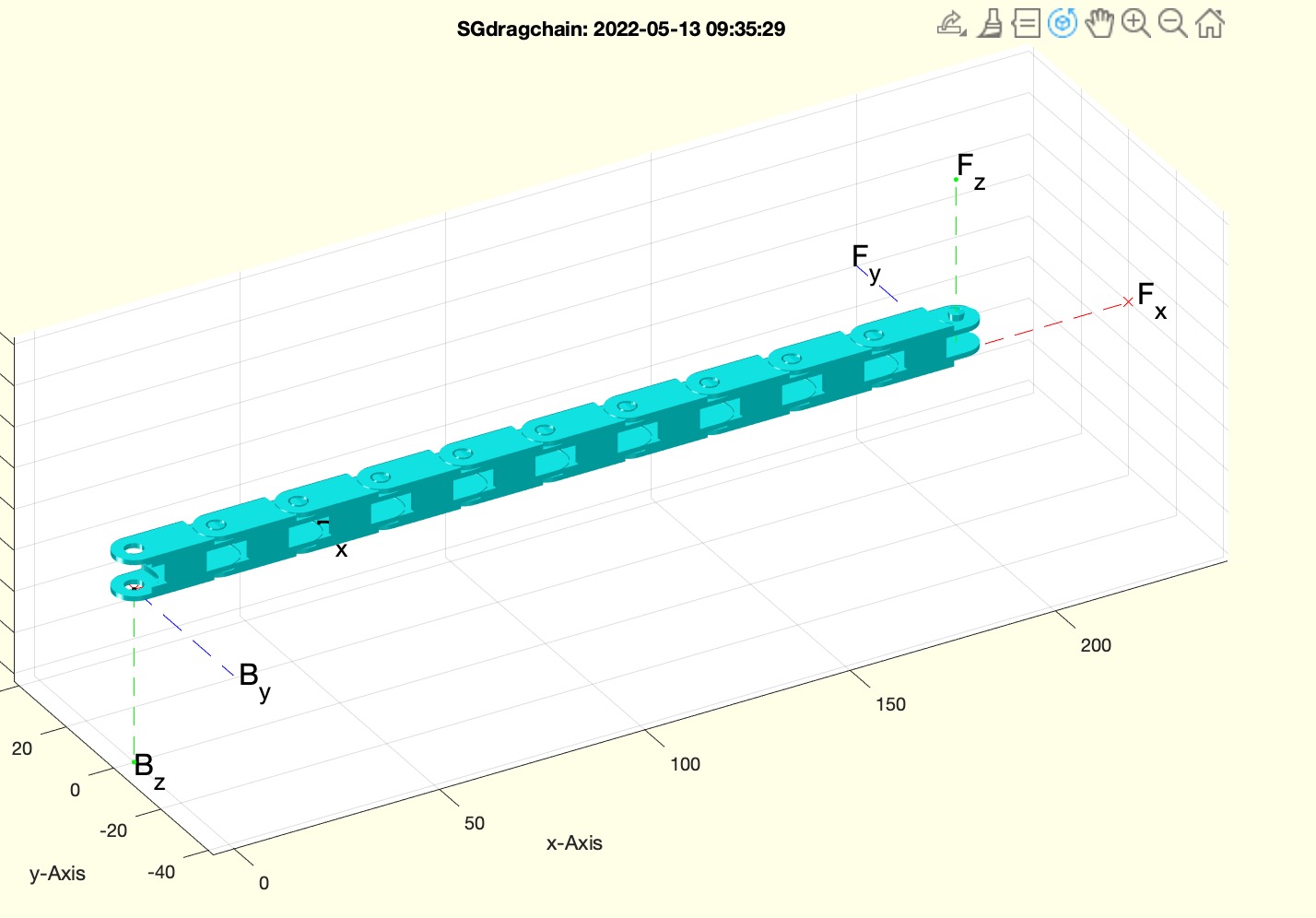
Syntax
SG=SGdragchain([L,R])
Input Parameter
Output Parameter
Copyright 2022-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This algorithm creates a 3D printable, already assembled drag chain using the SG-Library. The function is named SGdragchain and is designed to generate a series of interconnected elements that form a flexible chain.
Input Parameters
- L: The distance between the two axes of the drag chain elements. If not provided, it defaults to 10 mm.
- R: A vector specifying the height, width, and diameter of the pin for the drag chain elements. If not provided, it defaults to [9, 8, 3.5] mm.
Output
- SG: A structured geometry object representing the assembled drag chain.
Algorithm Steps
- Set the number of elements in the chain to
n = 60.
- Retrieve the input parameters
L and R using the getfuncparams function. Default values are used if parameters are not provided.
- Create the first drag chain element using
SGdragchainelement(L, R).
- Convert the element into a structured geometry object with
SGofSG.
- Extract the 'B' (back) reference point of the element using
SGTget.
- Initialize the drag chain with the first element.
- Iteratively create and align additional elements to form the chain:
- For each subsequent element, align it to the previous one using
SGtransrelSG with the 'alignT' method, aligning 'B' to 'F' (front) and rotating by pi radians.
- Add each new element to the chain.
- Extract the 'F' (front) reference point of the last element.
- Convert the entire chain into a single structured geometry object.
- Remove temporary geometry data with
SGTremove.
- Set the 'B' and 'F' reference points of the chain using
SGTset.
- If no output is requested, visualize the chain:
- Use
SGfigure to set up the viewing angle.
- Plot the chain with
SGTplotalpha.
- Write the chain to an STL file using
SGwriteSTL, rotating it by pi/2 radians around the x-axis.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-18 23:46. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21