SGdrillnotch
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Parametric Design
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.2, Creation date: 2022-08-10, Last change: 2025-09-15
sets a simple drilling notch on top of a surface
Description
Sometimes it is easier to drill a hole in a solid object using a drilling machine than to design a hole, since the exat diameter is unkown or flexible. In this cases you would need a drilling notch on the surface of the solid for a precise positioning of the drill's tip.
See Also: SGTdrill
, SGbox
Example Illustration
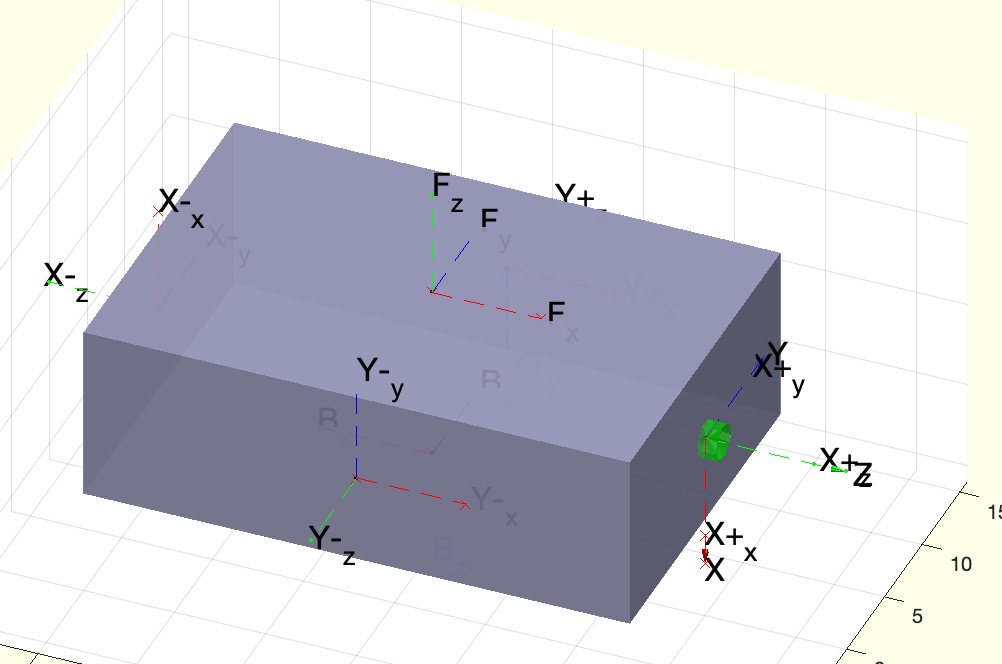
Syntax
SGdrillnotch([T,M])
Input Parameter
T: | | Frame or cell{Solid, Framename} |
M: | | metric diameter of the notch |
Examples
SGdrillnotch(eye(4),10)
SGdrillnotch({SGbox,'X+'},3)
Copyright 2022-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This algorithm is designed to create a drilling notch on the surface of a solid object. It is part of the SolidGeometry library and is used to facilitate precise positioning of a drill's tip.
Input Parameters
- T: This parameter can be a transformation matrix (frame) or a cell array containing a solid object and a frame name. It defines the position and orientation of the notch.
- M: This parameter specifies the metric diameter of the notch. It determines the size of the notch to be created.
Algorithm Steps
- The function begins by retrieving the input parameters using the
getfuncparams function. If no parameters are provided, default values are used: an identity matrix for T and a diameter of 3 for M.
- If
T is a cell array, the function checks if the specified solid and frame name exist using SGTget. If found, it updates T with the corresponding transformation matrix.
- The function creates a cylinder and a cone using the
SGcylinder and SGcone functions, respectively. Both shapes have a radius and height of M/3.
- The cone is then transformed and aligned with the cylinder using the
SGtransrelSG function. The cone is rotated by 180 degrees (pi radians) and aligned to the top of the cylinder with a slight offset.
- The combined shape (notch) is transformed according to the frame
T using the SGtransT function.
- If no output is requested, the function visualizes the notch using
SGfigure and SGTplotalpha. If a solid object was specified, it is also plotted.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:10. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21