SGfittingsample
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Samples
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.9, Creation date: 2020-08-08, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns a solid for fitting experiments
See Also: SGbox
, SGsample
Example Illustration
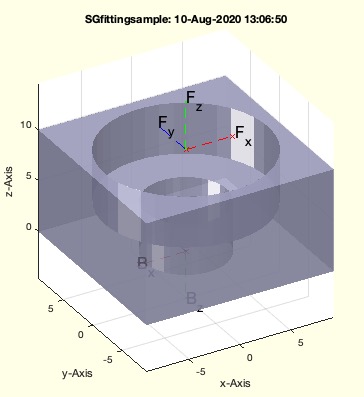
Syntax
SG=SGfittingsample([d])
Input Parameter
d: | | [d r1 r2 r3 ....] distance and radius |
Output Parameter
Examples
SGfittingsample([5 1 2 3])
Copyright 2020-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGfittingsample, is designed to create a solid geometry for fitting experiments. It is part of the SolidGeometry library and was introduced in version 4.9. The function takes a single input parameter and returns a solid geometry object.
Input Parameters
- d: A vector containing a distance and a series of radii. The first element is the distance, and the subsequent elements are radii.
Output Results
- SG: The resulting solid geometry object.
Algorithm Steps
- The function begins by creating a base solid geometry using the SGsubtract function. It subtracts a union of surfaces from a box.
- The input parameter 'd' is processed using the getfuncparams function, which extracts the first element as the distance and the rest as radii.
- The maximum radius is determined using the max function.
- A profile line (PL) is created using the PLshaft function, which takes the radii and distance as inputs.
- The profile line is then rotated to create a solid geometry using the SGofCPLrot function.
- The height of the solid is calculated based on the number of elements in 'd'.
- A circular profile is created using the PLcircle function, which is then extruded along the z-axis using the SGofCPLz function.
- The solid geometry is refined by subtracting the extruded circle from the rotated profile using the SGsubtract function.
- Surface edge points are removed using the SGremsurfedgepoints function to clean up the geometry.
- Transformations are applied to the solid geometry using the SGTset function to set the front and back transformations.
- If no output is requested, the function plots the solid geometry using SGfigure and SGTplotalpha functions.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 08:02. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21