SGinsertTslice
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Surfaces
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.3, Creation date: 2023-04-11, Last change: 2025-09-15
fnct that inserts required slice points into a surface before a stretch
Description
Similar to SGcutT but without the closing surface at the cutting plane.
See Also: SGcutT
, SGshort
Example Illustration
Syntax
[SG,SGU,SGO]=SGinsertTslice([SG,T,ct])
Input Parameter
SG: | | Solid Geometry |
T: | | Frame to cut by xy-plane |
ct: | | cutting mode if T is empty; see TofPcam |
Output Parameter
SG: | | Solid consisting of SGU and SGO (unified vertices by SGshort) |
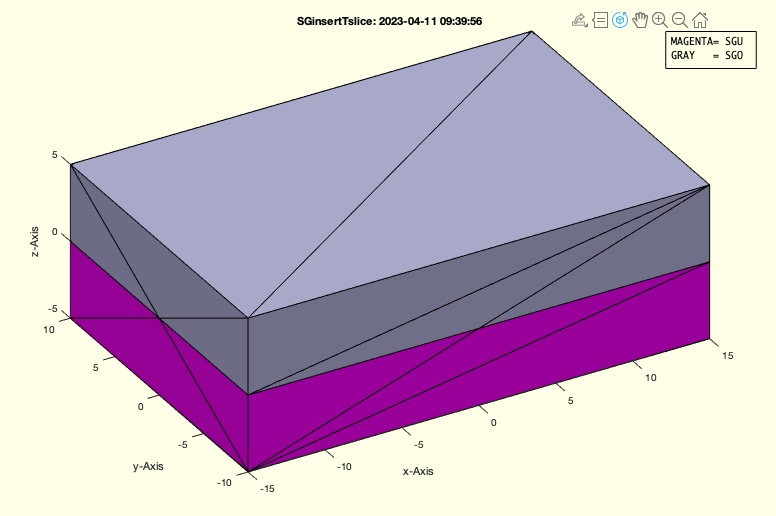
SGU: | | SGU lower part of wrt to frame T (Magenta) |
SGO: | | SGO upper part of wrt to frame T (Gray) |
Examples
SGinsertTslice(SGbox,eye(4))
Copyright 2023-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGinsertTslice, is designed to insert slice points into a surface before a stretch operation. It is part of the Solid Geometry (SG) library and was introduced in version 5.3. The function is similar to SGcutT but does not close the surface at the cutting plane.
Input Parameters
- SG: The solid geometry object that represents the 3D shape to be processed.
- T: A transformation matrix (frame) used to define the cutting plane by the xy-plane. If T is empty, the cutting mode is determined by the parameter ct.
- ct: The cutting mode used when T is empty. It is applicable only in interactive mode and is related to the TofPcam function.
Output Results
- SG: The resulting solid geometry consisting of unified vertices from SGU and SGO, processed by SGshort.
- SGU: The lower part of the solid geometry with respect to the frame T, represented in magenta.
- SGO: The upper part of the solid geometry with respect to the frame T, represented in gray.
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve the input parameters SG, T, and ct using the getfuncparams function. If SG is not provided, it defaults to SGofgca.
- Call the SGcutT function with the parameters SG, T, and ct to obtain the lower and upper parts of the solid geometry (SGU and SGO), along with indices Ufi and Ofi.
- Remove the faces from SGU and SGO that are indicated by the indices Ufi and Ofi, respectively.
- Concatenate SGU and SGO into a single solid geometry SG using the SGconcat function.
- Shorten the solid geometry SG using the SGshort function to unify vertices.
- If no output arguments are specified, visualize the result using SGfigure, plotannotation, SGplotalpha, and VLFLplotlight functions. SGU is displayed in magenta and SGO in gray.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:19. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21