SGreadPLY
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Import/Export
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.8, Creation date: 2019-12-19, Last change: 2025-09-14
reads in a Point Cloud in PLY Format an creates a surface model by marching cube
See Also: , VLreadPLY
, SGreadSTL
Example Illustration
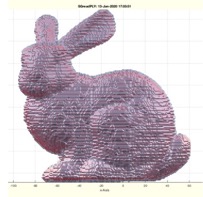
Syntax
[SG,VL,ptCloud]=SGreadPLY([FName,mag,res])
Input Parameter
FName: | | File Name or Empty for interactive selection |
mag: | | magnification of point cloud; default is 1000 |
res: | | resolution to avoid holes; default is 4 |
Output Parameter
SG: | | Solid Geoemtry |
VL: | | Vertex list |
ptCloud: | | original point cloud |
Examples
SGreadPLY('/Volumes/LUETH-WIN/WIN AIM Matlab Libraries/Point Clouds/bunny/reconstruction/bun_zipper.ply')
Copyright 2019-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGreadPLY, reads a point cloud from a PLY file and creates a surface model using the marching cubes algorithm. It is part of the SolidGeometry library.
Input Parameters
- FName: The file name of the PLY file. If empty, the function will prompt the user to select a file interactively.
- mag: The magnification factor for the point cloud. The default value is 1000.
- res: The resolution factor to avoid holes in the surface model. The default value is 4.
Output Results
- SG: The solid geometry created from the point cloud.
- VL: The vertex list extracted from the PLY file.
- ptCloud: The original point cloud data.
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve the file name (FName) from the input parameters or prompt the user to select a file if FName is empty.
- Retrieve the magnification factor (mag) from the input parameters, defaulting to 1000 if not provided.
- Retrieve the resolution factor (res) from the input parameters, defaulting to 4 if not provided.
- Read the point cloud data from the PLY file using the VLreadPLY function, applying the magnification factor.
- Calculate the minimum distance between vertices using the VLmindist function and determine a scaling factor (c) based on the maximum distance and resolution.
- Create a volumetric model (VM) from the vertex list (VL) using the VMofVL function with the calculated scaling factor.
- Generate a solid geometry (SG) from the volumetric model using the SGofVMisosurface function.
- Calculate the bounding box center points for both the original vertex list and the solid geometry using the sofBB and BBofVL functions.
- Translate the solid geometry to align its center point with the original vertex list using the SGtransP function.
- If no output arguments are specified, display the solid geometry and vertex list using SGfigure, VLplot, and SGplotalpha functions, and annotate the plot with the number of facets and vertices.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 08:07. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21