SGsweepTproj
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Surfaces
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.8, Creation date: 2019-09-10, Last change: 2025-09-14
sweeps the outer contour of a solid to create a swept solid
See Also: CPLsweep
, CPLofSGhull
Example Illustration
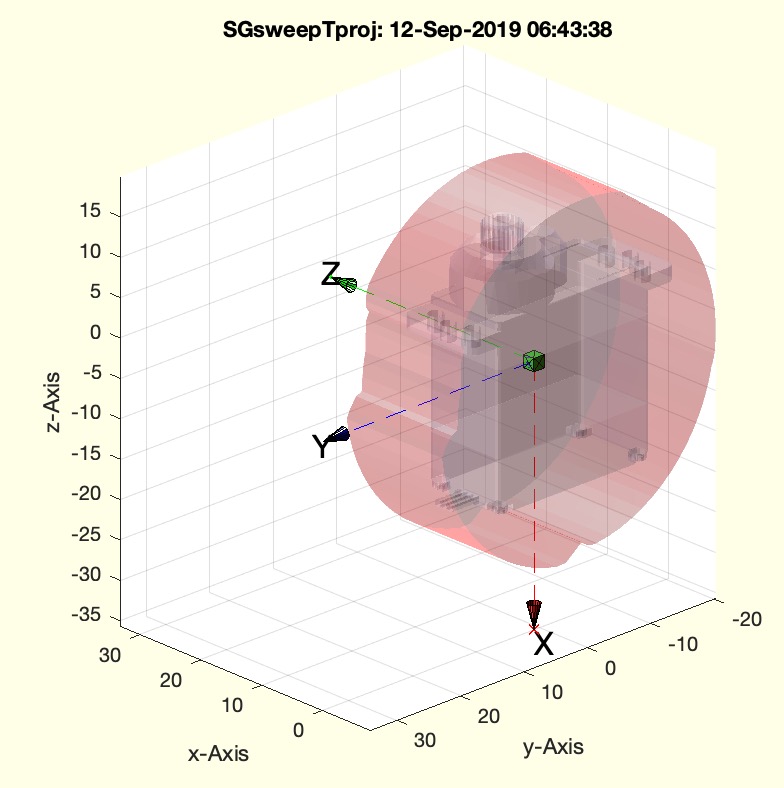
Syntax
SGS=SGsweepTproj(SG,[wt,T,b])
Input Parameter
SG: | | Solid Geometry |
wt: | | angle interval [wmin wmax] |
T: | | sweeping z-axis or HT Matrix or Frame char |
b: | | buffer to increase swept volume |
Output Parameter
SGS: | | Swept Solid Geometry |
Examples
SGsweepTproj(SGservosample(1),'',[1 0 0],2)
SGsweepTproj(SGservosample(1),'',[0 1 0],2)
SGsweepTproj(SGservosample(1),'',[0 0 1],2) % default
Copyright 2019-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGsweepTproj, is designed to sweep the outer contour of a solid to create a swept solid. Below is a detailed explanation of the algorithm and its parameters:
Input Parameters
- SG: The solid geometry to be swept.
- wt: The angle interval for sweeping, specified as [wmin wmax]. Default is [-pi/5, pi/5].
- T: The sweeping z-axis, a homogeneous transformation (HT) matrix, or a frame character. Default is [0 0 1].
- b: A buffer value to increase the swept volume. Default is 0.
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve the parameters
wt, T, b, and pc using getfuncparams. The default center point pc is calculated using centerVL(SG.VL).
- If
T is a character, it is assumed to be a frame name. The function SGTget retrieves the transformation matrix for this frame. If the frame is not defined, an error is thrown.
- If
T is a 3-element vector, it is converted to a transformation matrix using TofPez(pc,T).
- Transform the solid geometry
SG using the inverse of T with SGtransT, resulting in SGI.
- Calculate the bounding box and other parameters of
SGI using sofBB.
- Generate the contour polygon list (CPL) of the solid's hull using
CPLofSGhull.
- Remove straight lines with minimal angle using
CPLremstraightAmin with a threshold of 1e-3.
- Apply a buffer to the CPL using
CPLbuffer with the buffer value b.
- Sweep the CPL over the angle interval
wt using CPLsweep.
- Remove straight lines again using
CPLremstraightAmin.
- Create the swept solid geometry
SGS from the CPL using SGofCPLz, extending it by ss(3) + 2*b.
- Translate
SGS using SGtransP to adjust its position based on the bounding box and buffer.
- Transform
SGS back using SGtransT with the original transformation T.
- If no output is requested, plot the original and swept solids using
SGfigure, SGplotalpha, and tplot.
Output
- SGS: The resulting swept solid geometry.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:59. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21