TofBB
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Geometric Queries
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.1, Creation date: 2021-07-12, Last change: 2025-09-15
returns frames relative to bounding boxes
Description
Since may 1st, there is a difference between TofSG and TofBB !!!!!
calls the function TofSG of 27.11.2016
modified 2022-05-01
See Also: TofSG
Example Illustration
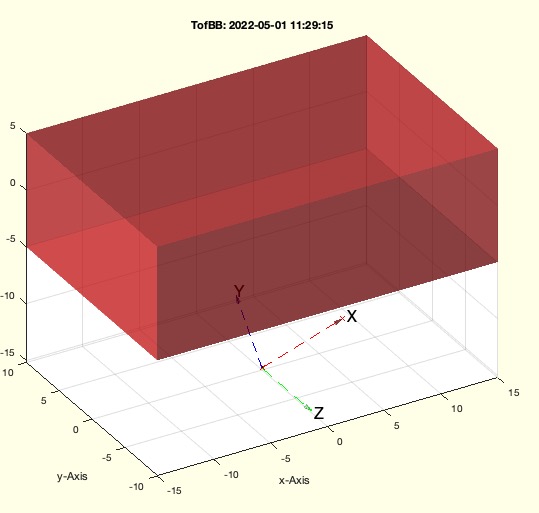
Syntax
T=TofBB(BB,[listofrel])
Input Parameter
BB: | | Bounding Box or cell list of Bounding boxes |
listofrel: | | list of relation such as 'under', {disp, ez, rotz} |
Output Parameter
T: | | Frame or cell list of frames |
Examples
clc; TofBB(SGbox,'under'); % simply under
clc; TofBB(SGbox,'under',10); % simply under with displacement 10
clc; TofBB(SGbox,'under',{10,[0 -1 0],pi/10}) % displacement 10, new ez, rotz
clc; TofBB(SGbox,'under',{10,[0 -1 0],[0 pi/10 0]}) % displacement 10, new ez, roty
Copyright 2021-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, TofBB, is designed to compute a homogeneous transformation matrix (HT matrix) relative to a nested solid geometry. It is part of the SG-Library, which deals with solid geometries. The function can handle different types of input, such as bounding boxes (BB), vertex lists (VL), or solid geometries (SG).
Input Parameters
- BB: This is the primary input, which can be a bounding box, vertex list, or solid geometry. The function determines the type based on the size of the input.
- varargin: This represents additional optional parameters, which can include relational terms like 'ontop', 'up', 'under', etc., or an ez-vector.
Output
- T: The output is a transformation matrix or a cell array of transformation matrices if the input is a cell array of solid geometries.
Algorithm Steps
- The function first checks the size of the input BB to determine its type:
- If BB is a 1x6 array, it is treated as a bounding box, and the function SGofBB is called to convert it to a solid geometry (SG).
- If BB has three columns, it is treated as a vertex list (VL), and the function BBofVL is used to convert it to a bounding box, which is then converted to SG.
- Otherwise, it is assumed to be a solid geometry, and the function SGofSG is used to ensure it is in the correct format.
- If the resulting SG is a cell array, the function iterates over each element, calling TofSG for each one and storing the results in a cell array T.
- If SG is not a cell array, TofSG is called directly with SG and any additional parameters.
- If no output is requested (nargout==0), the function visualizes the solid geometry and transformation using SGfigure, SGplot, and other plotting functions.
Visualization
If the function is called without output arguments, it will generate a 3D plot of the solid geometry and the transformation. This includes setting up the view, plotting the solid geometry, and adding lighting effects.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:46. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21