VMofSGweight
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - VM/Voxels
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.7, Creation date: 2019-07-30, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns a voxel model of a Solid Geoemtry using SGweight/SGisinterior
Description
The voxel size is adjusted automatically to maximize the resolution. The absolute position in space is lost. The orientation is unchanged.
See Also: SGweight
, SGvolume
, SGisInterior
, VMofSG
, SGofVMdelaunay
, SGofVMmarchcube
, VMofSG
, VMplot
Example Illustration
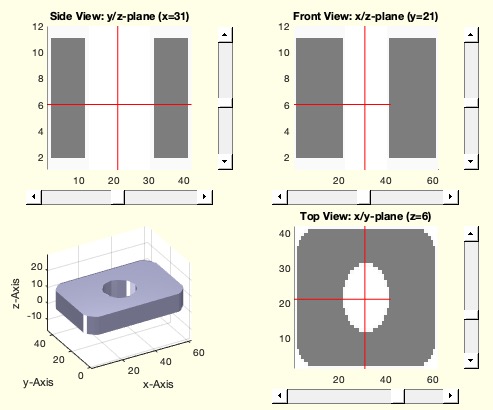
Syntax
[VM,sz,SGN,xl,yl,zl]=VMofSGweight(SG,[d])
Input Parameter
SG: | | Solid Geometry |
d: | | size of voxel |
Output Parameter
VM: | | Voxel Model |
sz: | | Voxel size |
SGN: | | Optional Solid by marching cube |
xl: | | list of x values of the Voxel Model |
yl: | | list of x values of the Voxel Model |
zl: | | list of x values of the Voxel Model |
Examples
VMofSGweight(SGsample(27),.5); VM=ans; whos VM
% VMdistancetoSG(VM)
Copyright 2019-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, VMofSGweight, is designed to convert a Solid Geometry (SG) into a Voxel Model (VM). The voxel size is automatically adjusted to maximize resolution, but the absolute position in space is lost, while the orientation remains unchanged.
Input Parameters
- SG: The Solid Geometry input that needs to be converted into a voxel model.
- d: The size of the voxel. If not provided, it is calculated as one-fiftieth of the bounding box size of the SG.
Output Results
- VM: The resulting Voxel Model.
- sz: The size of the voxel, represented as a vector [d d d].
- SGN: An optional solid generated by the marching cube algorithm.
- xl, yl, zl: Lists of x, y, and z values of the Voxel Model, respectively.
Algorithm Steps
- The function begins by ensuring the input SG is in the correct format using the function SGofSG.
- The size of the bounding box of the SG is determined using sofBB(SG).
- The voxel size 'd' is either taken from the input or calculated as one-fiftieth of the bounding box size.
- The SGweight function is called to generate the initial voxel model and the lists of x, y, and z values.
- The VMdistancetoSG function is applied to the voxel model to adjust it based on the distance to the SG.
- The voxel size is stored in the variable sz as [d d d].
- If the number of output arguments is zero or more than one, the SGN is generated using the SGofVMdelaunay function, applied to a thresholded version of the VM.
- If no output is requested, a figure is created using SGfigure, and the voxel model is plotted with VMplot. Additional visualization adjustments are made with camlightTL.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:56. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21