XPSEQS
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Artificial Intelligence
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.4, Creation date: 2023-11-29, Last change: 2025-09-15
Expert System implementing the first General Problem Solver (AI Programm)
Description
Order of parameters changed in Feb 2024
In contrast to XPSGPS, this function XPSEQS supports also equations based on $Var symbols. the delete list is applied before the add list, to allow the termination by adding removed facts
IF COND(STATE)==TRUE; NEWSTATE = [SETDIFF(STATE, DELLIST),ADDLIST)
Since 2024, also Equations or matlab code can be evaluated such as "$A==4" or "$L==$R-1"
See Also: XPSblocksworld
, XPSGPS
, XPSconditionfindneval
, XPSslidingpuzzle
Example Illustration
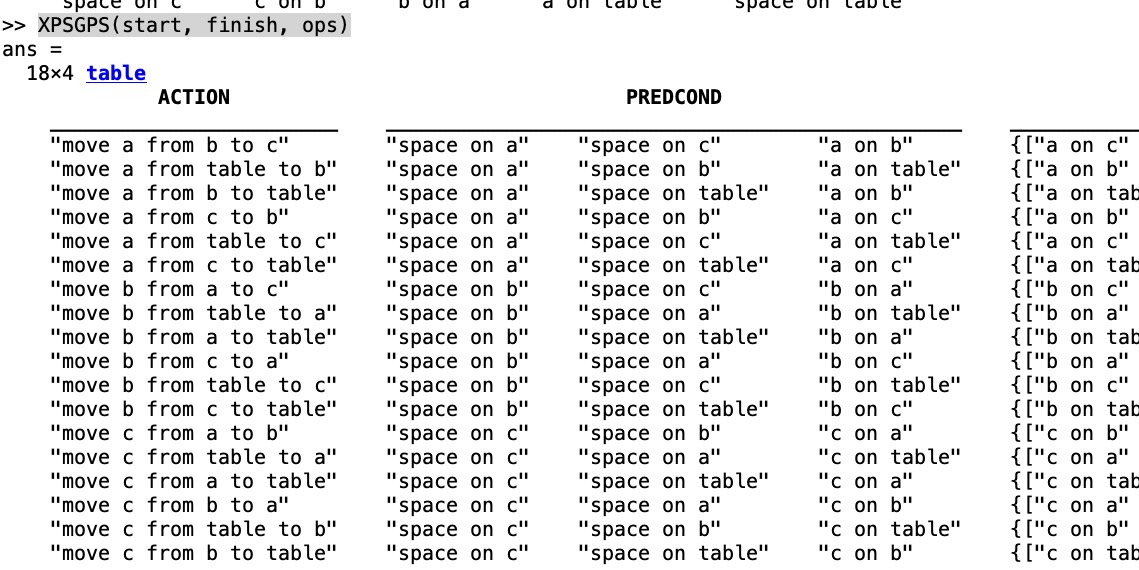
Syntax
[solut,endstate,solutstates,plan]=XPSEQS([ops,start,finish,"debug","first"])
Input Parameter
ops: | | cell list [n x 4] describing action-name, precondition, add-state, diff-state |
start: | | string array describing the start state |
finish: | | string array describing the final state |
"debug": | | if used, the progress is shown |
"first": | | if used, the first solution is returned |
Output Parameter
solut: | | solutions |
endstate: | | end state of the solutioin |
solutstates: | | state change of the solutions |
plan: | | all plans generated |
Examples
clc; [ops,start,finish]=XPSblocksworld % Example efinitions of operators start-state and goal-state
opsnew={["move $A from $B to $C"], ["space on $A", "space on $C", "$A on $B"], ["$A on $C", "space on $B" "space on table"], ["$A on $B", "space on $C"]} % ACTION, COND, ADD, DEL
XPSEQS(ops, start, finish);
XPSEQS(opsnew, start, finish);
References
- Norvig, Peter (1991): Paradigms of Artificial Intelligence Programming, Morgan Kaufmann Publisher, San Mateo, CA, USA
Copyright 2023-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21