XPSruleswrite
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Artificial Intelligence
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.4, Creation date: 2023-12-14, Last change: 2025-09-15
writes rules into an excel sheet
Description
The format of the rules will may change over Time
See Also: XPSrulesread
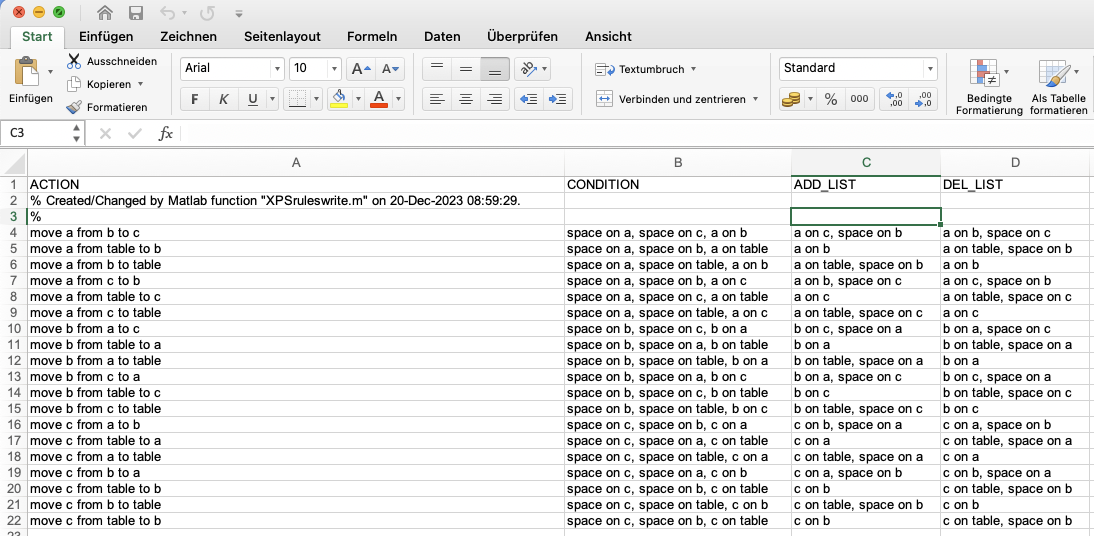
Example Illustration
Syntax
rname=XPSruleswrite(ops,[fname])
Input Parameter
ops: | | operators |
fname: | | filename |
Output Parameter
rname: | | rules full file name |
Examples
[ops,start, goal]=XPSblocksworld; XPSruleswrite(ops,'TEST.XLS')
Copyright 2023-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, XPSruleswrite, is designed to write a set of rules into an Excel sheet. It is part of the SolidGeometry library and was introduced in version 5.4. The function takes operators and an optional filename as input parameters and outputs the full filename of the rules written.
Input Parameters
- ops: This parameter represents the operators that will be written into the Excel sheet. It is expected to be in a format that can be converted into a cell array of strings.
- fname: This is an optional parameter representing the filename where the rules will be saved. If not provided, the default filename 'XPSRULE.xls' is used.
Output
- rname: This is the full file name of the Excel sheet where the rules have been written. It includes the path to the file.
Algorithm Steps
- The function begins by determining the filename using the
getfuncparams function. If a filename is not provided, it defaults to 'XPSRULE.xls'.
- The operators (
ops) are converted into a cell array of strings using the stringcellarray2charcell function, with a comma as the delimiter.
- The converted cell array is then written into an Excel sheet using the
SGwritetable function. This function takes the filename and a table created by array2tableTL, which includes columns for 'ACTION', 'CONDITION', 'ADD_LIST', and 'DEL_LIST'.
- The full path of the written file is constructed by concatenating the current working directory with the filename.
- If no output argument is specified (
nargout==0), the function automatically opens the Excel file using the openbydoubleclick function.
This function is useful for exporting rule-based data into a structured Excel format, which can be easily shared and analyzed.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-18 23:22. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21