atomiccovalentradius
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Auxiliary function
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.8, Creation date: 2019-12-13, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns the atomic radius or the covalent bond distance of two atoms determined from it
Description
In addition to the Van der Waals radius there is the simple atomic radius. This is used to calculate the covalent formation distance of two atoms.
See Also: VanDerWaalsRadius
Example Illustration
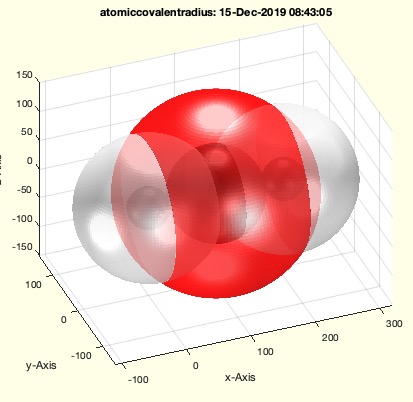
Syntax
[R,SG]=atomiccovalentradius([Str])
Input Parameter
Str: | | Kovalent Bond String such as 'H-O-H' |
Output Parameter
R: | | List of Atomic Radius and Van der Waals Radius |
SG: | | List of Solid Geometries fitting to the Radius table |
Examples
atomiccovalentradius('H-O-H')
Copyright 2019-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function calculates the atomic radius and covalent bond distance of atoms specified in a string format. It uses the Van der Waals radius to determine these values.
Input Parameters
- Str: A string representing a covalent bond, such as 'H-O-H'.
Output Results
- R: A list containing the atomic radius and Van der Waals radius for each atom in the input string.
- SG: A list of solid geometries corresponding to the radius table.
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve the input parameter
Str using getfuncparams function.
- Split the input string
Str into individual atoms using delimiters '-' and '='.
- Determine the number of atoms
n in the string.
- For each atom in the string:
- Call
VanDerWaalsRadius function to get the Van der Waals radius vr, solid geometry sg, and covalent radius cr.
- Store the covalent radius
cr in the first column of R.
- Store the Van der Waals radius
vr in the second column of R.
- Store the solid geometry
sg in SG.
- If no output arguments are specified:
- Create a new figure using
SGfigure and set the view angle.
- Plot the first solid geometry with transparency using
SGplotalpha.
- Initialize a distance variable
d to zero.
- For each subsequent atom:
- Update the distance
d by adding the covalent radii of the current and previous atoms.
- Translate the solid geometry of the current atom by the distance
d using SGtransP.
- Plot the translated solid geometry with transparency.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 01:22. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21