readtable2code
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - CODING/DEVELOP
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.0, Creation date: 2021-01-24, Last change: 2025-09-15
reads tables and creates strings in the command window that can be used as code in matlab m files
Description
Helpful to insert EXCEL Sheet information in m files
See Also: DIN4AMtemperature
Example Illustration
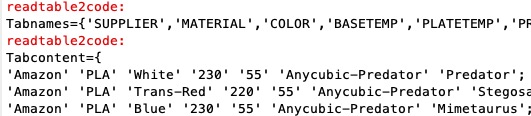
Syntax
readtable2code(fname)
Input Parameter
fname: | | file name of a table such as "temptable.xls" |
Examples
readtable2code('DIN4AMtemperature.xls')
Copyright 2021-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This algorithm is a MATLAB function named readtable2code that reads a table from a file and generates MATLAB code strings that can be used in MATLAB m-files. The function is particularly useful for converting Excel sheet data into MATLAB code.
Input Parameters
- fname: The file name of a table, such as "temptable.xls". This is the only input parameter and should be a string representing the file path or name.
Algorithm Steps
- The function first checks if the file specified by
fname exists using the exist function. If the file exists, it proceeds; otherwise, it does nothing.
- If the file exists, it uses the
which function to get the full path of the file and assigns it back to fname.
- A debug print statement is executed to indicate the file being read, using
dbprintf.
- The function reads the table from the file using
readtable with the format set to 'auto'. This reads the data into a table variable RTab.
- The variable names of the table are extracted into
Taborder using RTab.Properties.VariableNames.
- The table is converted to a cell array
TT using table2cell.
- A string
Header is initialized to store the variable names in a format suitable for MATLAB code. It starts with 'Tabnames={'.
- A loop iterates over the variable names in
Taborder. For each name, it appends it to Header in the format 'name', or 'name'} for the last element.
- A string
C is initialized to store the table content in a format suitable for MATLAB code. It starts with 'Tabcontent={' followed by a newline.
- Nested loops iterate over each element of the cell array
TT. For each element, it appends it to C in the format 'value' or 'value'; for the last element in a row, followed by a newline.
- The string
C is completed with '};' to close the MATLAB cell array syntax.
- Debug print statements output the
Header and C strings, which represent the MATLAB code for the table's variable names and content, respectively.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:11. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21