CPLextendbyPL
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - CPL/Closed Polygon Lists
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.1, Creation date: 2021-12-26, Last change: 2025-09-15
extends a CPL outline contour by some points
Description
used in fourBarposesyntheses with constraint "EXTEND CPLM"
See Also: CPLadd
, CPLaddauxpoints
, CPLrack4PL
Example Illustration
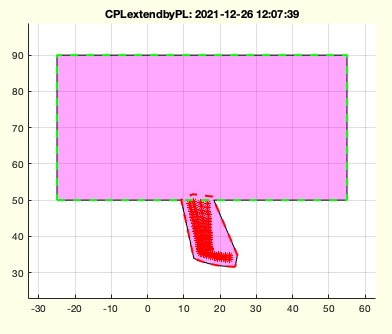
Syntax
CPLC=CPLextendbyPL(CPL,PL,[lim,buf])
Input Parameter
CPL: | | Exisintg CPL |
PL: | | New Points |
lim: | | limit until extension default is s |
buf: | | buffer arount PL; default is s/10 |
Output Parameter
Examples
CPLextendbyPL(CPLsample(6),[-10 -10],'',1)
CPLextendbyPL(CPLsample(12),[-10 -10],'',1)
Copyright 2021-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, CPLextendbyPL, extends an existing closed polygon list (CPL) by adding new points (PL) to it. The function is part of the SolidGeometry library and is used in four-bar pose synthesis with the constraint "EXTEND CPLM".
Input Parameters
- CPL: The existing closed polygon list that needs to be extended.
- PL: A set of new points that may be added to the CPL.
- lim: The limit until which the extension is allowed. If not provided, it defaults to the smallest positive value in the bounding box of the CPL.
- buf: A buffer around the new points (PL). If not provided, it defaults to one-tenth of the smallest positive value in the bounding box of the CPL.
Output
- CPLC: The new contour that results from extending the original CPL with the new points.
Algorithm Steps
- Calculate the bounding box of the CPL using
BBofCPL and determine the smallest positive dimension s.
- Ensure the new points (PL) are unique by removing duplicate rows.
- Determine the limit (
lim) and buffer (buf) values using getfuncparams. If not provided, default values are used.
- Check which points in PL are inside the CPL using
isInteriorofCPL. Separate these points into PLO (inside) and PL (outside).
- Find the nearest cluster of points in PL using
nearestcluster with a quarter of s as the distance threshold.
- If a cluster is found, buffer the convex hull of the cluster using
CPLbuffer and fill the gap between the original CPL and the new buffer using CPLconvexhullfillgap.
- If no cluster is found, the original CPL is returned as the result.
- If no output is requested, plot the results using
SGfigure and various plotting functions to visualize the original CPL, new points, and the extended contour.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:48. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21