CPLofouterregionboundary
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - CPL/Closed Polygon Lists
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 4.5, Creation date: 2019-02-09, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns the outer boundary of regions of CPL
Description
Find out the difference to CPLfillinside
CPSplot(CPLfillinside(CPLsample(12)))
CPSplot(CPLofouterregionboundary(CPLsample(12)))
See Also: CPLfillinside
, CPLgrow
, CPLbuffer
Example Illustration
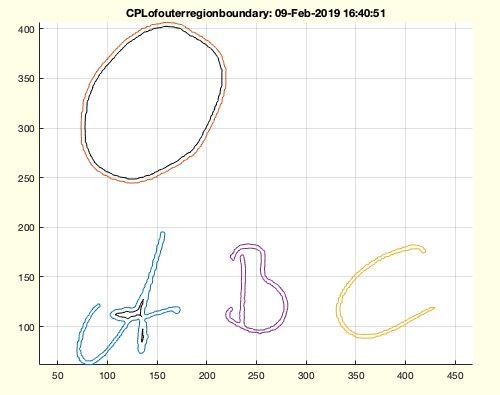
Syntax
CPLN=CPLofouterregionboundary(CPL,[sline])
Input Parameter
CPL: | | Closed polygon line |
sline: | | additional line thickness; default is 1% of BB of CPL |
Output Parameter
CPLN: | | outer boundary of regions |
Examples
CPSplot(CPLfillinside(CPLsample(12)))
CPSplot(CPLofouterregionboundary(CPLsample(12)))
Copyright 2019-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, CPLofouterregionboundary, is designed to compute the outer boundary of regions defined by a closed polygon line (CPL). It is part of the SolidGeometry library and was introduced in version 4.5.
Input Parameters
- CPL: A closed polygon line, which is the primary input for the function.
- sline: An optional parameter that specifies additional line thickness. If not provided, it defaults to 1% of the bounding box (BB) of the CPL.
Output Results
- CPLN: The outer boundary of the regions.
- CPLO: The outer boundary with an optional buffer applied, if
sline is greater than 0.
Algorithm Steps
- Calculate the default line thickness
s as 1% of the bounding box area of the CPL.
- If
sline is provided and greater than 0, update s to be the square of sline.
- Check if the CPL is empty. If it is, return empty arrays for
CPLN and CPLO.
- Convert the CPL into a
polyshape object without simplifying it.
- Sort the boundaries of the polyshape by area in descending order.
- Filter out regions with an area smaller than
s.
- Initialize an array
ni to store the number of boundary points for each region.
- Iterate over each region to populate
ni with the number of boundary points.
- Initialize
CPLN to store the coordinates of the outer boundary.
- Iterate over each region again to fill
CPLN with boundary coordinates, separating regions with NaN values.
- If
sline is greater than 0, compute CPLO by buffering CPLN with a negative sline and rounding the corners.
- If no output arguments are specified, plot
CPLN and CPLO using SGfigure and CVLplot.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 08:14. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21