PLspiral
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - PL/Point Lists
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 2.7, Creation date: 2015-09-24, Last change: 2025-09-14
return the PL of a spiral
Description
For 3D use VLhelix
See Also: PLcircle
, PLcircseg
, PLevolvente
, PLgearDIN
, PLkidney
, PLrand
, PLsquare
, PLstar
Example Illustration
Syntax
PL=PLspiral(RI,RO,[wm,n])
Input Parameter
RI: | | Inner Diameter |
RO: | | Outer Diameter |
wm: | | Desired angle; default is 2pi |
n: | | number of points; default is nofrd((RO+RI)/2)/2pi*wm |
Output Parameter
Examples
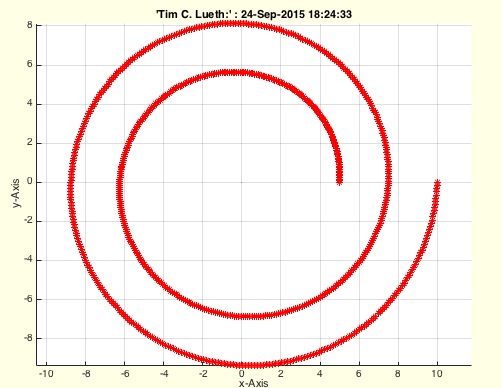
Two turn spiral
PLspiral(5,10,4*pi)
Copyright 2015-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, PLspiral, generates a point list representing a spiral shape. It is part of the SG-Library and was created by Tim Lueth. The function is designed to work in 2D, and for 3D applications, the VLhelix function is recommended.
Input Parameters
- RI: Inner Diameter - This is the starting radius of the spiral.
- RO: Outer Diameter - This is the ending radius of the spiral.
- wm: Desired angle - This parameter defines the angular extent of the spiral. The default value is
2*pi, which corresponds to a full circle.
- n: Number of points - This parameter determines how many points will be used to define the spiral. The default is calculated based on the average of
RO and RI, divided by 2*pi and multiplied by wm.
Output Results
- PL: Point list [nx2] - This is the output of the function, a list of points in 2D space that define the spiral.
Algorithm Steps
- Initialize
wm to 2*pi. If a third argument is provided and not empty, set wm to this value.
- Calculate the default number of points
n using the formula: n = nofrd(max(RO,RI))/(2*pi)*wm. If a fourth argument is provided and not empty, set n to this value.
- Create a vector
w that represents the angular positions from 0 to wm with n points.
- Create a vector
r that represents the radial positions from RI to RO with n points.
- Generate the point list
PL by calculating the cosine and sine of the angles in w, and scaling them by the radial distances in r.
- If no output is requested, plot the spiral using
SGfigure and PLplot functions, setting the view to a top-down perspective.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 00:57. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21