SGcompass
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Modeling function
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.1, Creation date: 2021-09-12, Last change: 2025-08-18
creates a desktop housing for the magnetic compass (look like a Gyro compass)
See Also: SGjuicermachineclip
Example Illustration
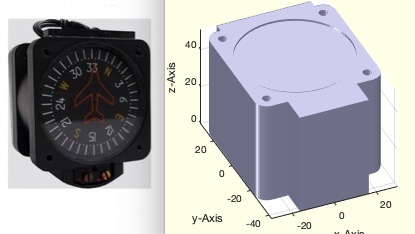
Syntax
SG=SGcompass
Output Parameter
SG: | | Just returns the geometry of the compass |
Examples
SGcompass
Copyright 2021-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGcompass, creates a 3D model of a compass using a series of geometric transformations and operations. Below is a detailed explanation of the algorithm and its parameters:
Input Parameters
The function SGcompass does not take any input parameters. It operates with predefined values and functions to generate the compass geometry.
Algorithm Steps
- Create Radial Edges:
- Use
CPLradialEdges on a square defined by PLsquare([60 60]) to create radial edges with 6 divisions.
- Create Circular Pattern:
- Generate a circular pattern using
PLcircle with a radius of 1.5 + slfit('s').
- Copy this pattern using
CPLcopypattern with a grid of [2 2] and spacing of [48 48].
- Align the pattern using
CPLtransrelCPL with the 'incenter' option.
- Combine Geometries:
- Subtract the circular pattern from the radial edges using
CPLtransrelCPL with 'incenter' and '-'.
- Add a square of size
[45 4] on top using CPLtransrelCPL with 'ontop' and '+'.
- Add another square of size
[33 13] underneath using CPLtransrelCPL with 'under' and '+'.
- Create 3D Geometry:
- Convert the 2D geometry to 3D using
SGofCPLz with a height of 51.
- Subtract Cylinder:
- Subtract a cylinder with a radius of 27 and height of 2 from the top using
SGsubtract with 'ontop' and -1.
- Optional Visualization:
- If no output is requested (
nargout==0), plot the geometry using SGfigure and SGplotalpha with a white color ('w').
Output
The function returns the 3D geometry of the compass as SG.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-18 23:51. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21