SGgearchainstraight
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Kinematics and Frames
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.4, Creation date: 2024-05-17, Last change: 2025-09-15
brings all the axes of a gear chain in a straight line
Description
Opposite of SGgearchainrotate
written during ICRA 2024 Yokohama
See Also: SGgearchain
, SGgearchainwindup
, SGgearchainrotate
Example Illustration
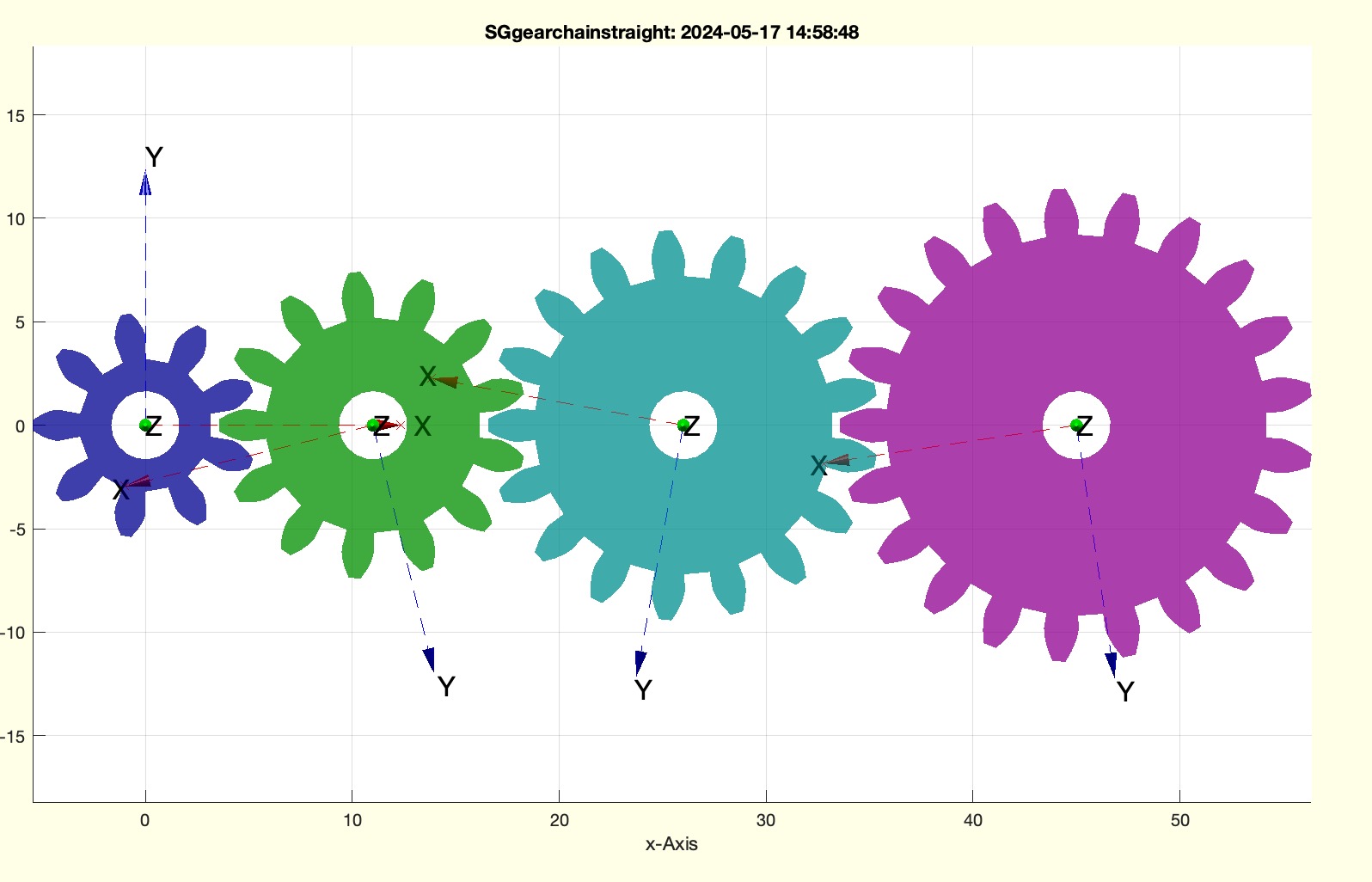
Syntax
SG=SGgearchainstraight(SG,f)
Input Parameter
SG: | | Cell list of gear wheel with base frames 'B' |
f: | | array of gear ration with respect to the 1st one f(1)==1 |
Output Parameter
SG: | | cell array of gears with modified position and rotation |
Examples
SGgearchain(1,[9 13 17 21],'',0); [SG,TL,f,SGR]=SGgearchain(1,[9 13 17 21],'','',0); % a gear chain
SGgearchainrotate(SG,f,[pi/2]); SHN=ans;
SGgearchainstraight(SGN,f)
Copyright 2024-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGgearchainstraight, is designed to align all the axes of a gear chain in a straight line. It is the opposite of the function SGgearchainrotate.
Input Parameters
- SG: A cell list of gear wheels with base frames 'B'.
- f: An array of gear ratios with respect to the first one, where
f(1) == 1.
- varargin: Additional optional parameters.
Output Results
- SG: A cell array of gears with modified position and rotation.
- SGA: An optional output that stores additional parameters.
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve additional function parameters using
getfuncparams and store them in SGA.
- Determine the number of gear wheels using
numel(SG) and store it in nw.
- If
SGA is empty, initialize it as a cell array with the same number of elements as SG.
- Iterate over each gear wheel starting from the second one:
- Retrieve the base frame of the previous gear wheel using
SGTget and set its rotation part to the identity matrix.
- Retrieve the base frame of the current gear wheel using
SGTget and set its rotation part to the identity matrix.
- Calculate the transformation matrix
TR from the previous to the current gear wheel.
- Compute the angle
W needed to align the gear axes using atan2.
- Rotate the gear chain from the current gear wheel onwards using
SGgearchainrotate with the calculated angle W.
- If no output is requested (
nargout == 0), visualize the gear chain:
- Calculate the size of the bounding box using
sofBB.
- Create a figure with a specific view using
SGfigure.
- Plot each gear wheel with transparency using
SGplotalpha and plot the base frame using tplot.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:54. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21