SGiso4762
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - ENG-Components
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 3.0, Creation date: 2016-11-21, Last change: 2025-09-14
SG of Hexagon socket set screw with cylindric head
Description
returns a solid geometry of a "Hexagon socket set screw with flat point" related to DIN912 or ISO4762
See Also: DINhelp
, DIN913
, SGiso4026
, DIN912
, DIN336
Example Illustration
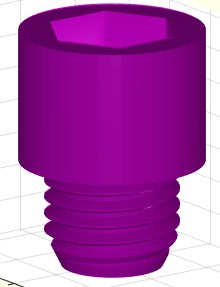
Syntax
SG=SGiso4762(M,L)
Input Parameter
M: | | Diameter (millimeter) |
L: | | Length (millimeter) |
Output Parameter
SG: | | Solid geoemetry of Hexagon socket set screw with flat point |
Copyright 2016-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGiso4762, generates a solid geometry of a hexagon socket set screw with a cylindrical head, following the standards of DIN912 or ISO4762. The function is part of the SG-Library and was created by Tim Lueth on November 21, 2016.
Input Parameters
- M: Diameter of the screw in millimeters.
- L: Length of the screw in millimeters.
Output
- SG: Solid geometry of the hexagon socket set screw with a flat point.
Algorithm Steps
- The function begins by calling another function, SGiso4026, with parameters M, L, and a boolean value 'false'. This function is assumed to generate a basic solid geometry of a screw.
- The function DIN912 is called with the parameter M to retrieve a set of dimensions, stored in the variable T.
- A polyline (PL) is created using the function PLcircle, which generates circular profiles. The first circle has a radius of T(6)/2.2, and the second circle has a radius of T(2)/2 + 0.1, with 6 segments.
- The function SGofCPLz is used to create solid geometries from the polylines. SGH is created with the polyline PL and height T(3). SGB is created with a circle of radius T(6)/2.2 and height T(5)-T(3).
- The function SGontop is used to position SGB on top of the initial solid geometry SG, with an offset of -0.1. Similarly, SGH is positioned on top of SGB with the same offset.
- The function SGcat2 concatenates the geometries SG, SGB, and SGH into a single solid geometry.
- If no output is requested (nargout==0), the function SGfigure is called to create a figure, and SGplot is used to plot the solid geometry in magenta ('m'). The view is set to (0,0).
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-18 23:04. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21