SGlinkwall
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - SG/Solids
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 1.0, Creation date: 2012-11-18, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns a solid geometry of a plain wall and attaches it to a solid geometry
Description
This function uses TofVLULez to find a corresponding union of the body. If it fails, no wall, nor attachment will be generated
Example Illustration
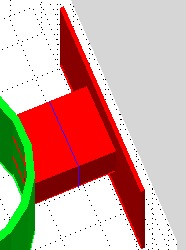
Syntax
SGW=SGlinkwall(SGA,n1,dist,sz,sx,sy)
Input Parameter
SGA: | | Solid geometry that should get a wall |
n1: | | ez vector points into the wall direction |
dist: | | distance, the wall should be created |
sz: | | depth of the wall |
sx: | | size in x |
sy: | | size in y |
Output Parameter
SGW: | | Solid geometry of wall and linking structure |
Copyright 2012-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGlinkwall, is designed to create a solid geometry of a plain wall and attach it to an existing solid geometry. It is part of the SG-Library and was developed by Tim Lueth in 2012. The function uses a specific procedure to find a corresponding union of the body, and if it fails, no wall or attachment will be generated.
Input Parameters
- SGA: The solid geometry that should receive a wall.
- n1: A vector indicating the direction into which the wall should be constructed.
- dist: The distance at which the wall should be created from the original geometry.
- sz: The depth of the wall.
- sx: The size of the wall in the x-direction.
- sy: The size of the wall in the y-direction.
Output Results
- SGW: The resulting solid geometry of the wall and linking structure.
Algorithm Steps
- Calculate a homogeneous transformation (HT) matrix for a surface with direction ez using the function
TofVLULez with inputs SGA.VL, SGA.UL, and n1.
- Plot the transformation matrix
TA using tplot.
- Generate a plate at the specified distance as a second body using
VLFLboxT with inputs TA, sz, sx, sx, and dist.
- Calculate the opponent HT matrix
TB using TofVLULez with inputs SGB.VL, UL, and -n1.
- Plot the transformation matrix
TB using tplot.
- Determine the link dimensions
ld and lw as half of the minimum of sx and sy, and a constant value of 2, respectively.
- Calculate a straight structural link between the original and new geometries using
SGlinkstraight with inputs SGA, SGB, TA, TB, ld, and lw.
- If the resulting geometry
SGW is not empty, concatenate it with SGB using SGcat. Otherwise, set SGW to an empty array.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 01:38. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21