SGtransrel
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Spatial Relations
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.4, Creation date: 2024-08-14, Last change: 2025-09-15
returns a spatial transformed solid using SGtransrelSG
Description
same as SGN=SGtransrelSG (SG,'',varargin{:})
The relative movements is with respect to the origin
See Also: SGtransrelSG
Example Illustration
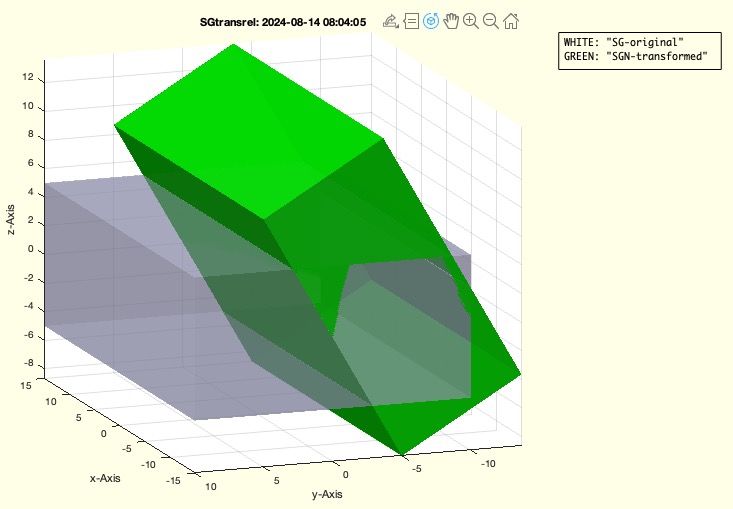
Syntax
SGN=SGtransrel(SG,[]);
Input Parameter
Output Parameter
SGN: | | Spatially transformed solid |
Examples
SGtransrel(SGbox,'ontop','rotx',pi/3)
Copyright 2024-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGtransrel, is designed to perform spatial transformations on a solid geometry object, referred to as SG. The function is part of the SolidGeometry library and was developed by Tim Lueth. It is used to apply relative movements to a solid with respect to the origin.
Input Parameters
- SG: This is the solid geometry object that you want to transform.
- varargin: This represents a variable-length input argument list. It allows the function to accept additional parameters that specify the type of transformation to be applied to the solid geometry.
Output Results
- SGN: This is the spatially transformed solid geometry object that results from applying the specified transformations to
SG.
Algorithm Steps
- The function first checks if the first element of
varargin is a solid geometry object using the isSG function. If it is, an error is raised instructing the user to use the SGtransrelSG function instead.
- If the check passes, the function calls
SGtransrelSG with the original solid geometry SG, an empty string, and the additional transformation parameters provided in varargin. This function performs the actual transformation and returns the transformed solid SGN.
- If no output argument is specified (i.e.,
nargout == 0), the function proceeds to visualize the transformation:
- It calls
SGfigure to set up a figure window with a specified range.
- It uses
SGplotalpha to plot the original solid SG in white with 50% transparency.
- It plots the transformed solid
SGN in green with 90% transparency.
- It adds annotation text to the plot to label the original and transformed solids.
Example Usage
An example call to this function is SGtransrel(SGbox,'ontop','rotx',pi/3), which would apply a rotation transformation to the solid geometry SGbox.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-18 23:30. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21