VLFLspacer
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Modeling function
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 1.0, Creation date: 2013-04-29, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns a 2½ D solid geometry of a spacer
Description
Tim C. Lueth, Franz Irlinger: "Berechnete Erzeugung von dreidimensionalen Oberflächenmodellen im STL-Format aus der Beschreibung planarer Mechanismen für die Generative Fertigung durch Selektives-Lasersintern [Computational 3D Surface Generation of Planar Mechanismus using STL File Format for Generative Manufacturing by Selective Laser Sintering]", angenommener Beitrag im Konferenzband 10. Kolloquium Getriebetechnik, TU Ilmenau, Sep. 11-13, 2013, pp 1-18.
See Also: VLFLsnapfit
, VLFLshaft
, VLFLhollowsnapaxle
, VLFLcat
, TofDPhiH
, VLtransT
, VLFLbolt
, VLFLlinkage
, VLFLwriteSTL
, VLFLofPLELz
, VLFLplot
Example Illustration
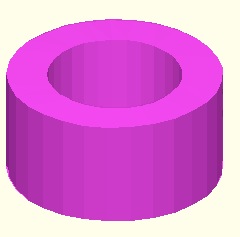
Syntax
[VL,FL]=VLFLspacer(RA,RI,H)
Input Parameter
RA: | | Outer Radius |
RI: | | Inner Radius |
H: | | Height |
Output Parameter
VL: | | Vertex list |
FL: | | Facet list |
Copyright 2013-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, VLFLspacer, generates a 2.5D solid geometry of a spacer using the outer radius (RA), inner radius (RI), and height (H) as input parameters. The function returns a vertex list (VL) and a facet list (FL).
Input Parameters
- RA: Outer Radius of the spacer.
- RI: Inner Radius of the spacer.
- H: Height of the spacer.
Algorithm Steps
- Set the number of segments
n to 16, then adjust it using the function nofrd(RA) which likely determines an appropriate number of segments based on the outer radius.
- Calculate the angular width
dw for each segment as 2*pi/n.
- Initialize the angle
w to -dw/2.
- Create the outer polygon
PLA by iterating over n segments, incrementing w by dw each time, and calculating the x and y coordinates using cos(w)*RA and sin(w)*RA.
- Create the inner polygon
PLI similarly, using RI instead of RA.
- Define the edge list for the outer polygon
ELA as a sequence of indices from 1 to n, wrapping around to form a closed loop.
- Define the edge list for the inner polygon
ELI similarly, but in reverse order to maintain the correct orientation.
- Combine the outer and inner polygons into a single point list
PL and edge list EL.
- Call the function
VLFLofPLELz with PL, EL, and H to generate the vertex list VL and facet list FL.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 00:42. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21