VLprojection2SG
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Analytical Geometry
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.0, Creation date: 2020-12-08, Last change: 2025-09-15
projects a Vertex list in parallel projection to a solid
Description
this is not the 1st implementation ;-) but it was easier to implement than to search for the name
correct name would be CVLof
See Also: VLprojection
Example Illustration
Syntax
VLN=VLprojection2SG(SG,VL,ez)
Input Parameter
SG: | | Solid to project to |
VL: | | Vertex list |
ez: | | normal vector |
Output Parameter
VLN: | | Corresponding projection points; nan if there is no projection point |
Examples
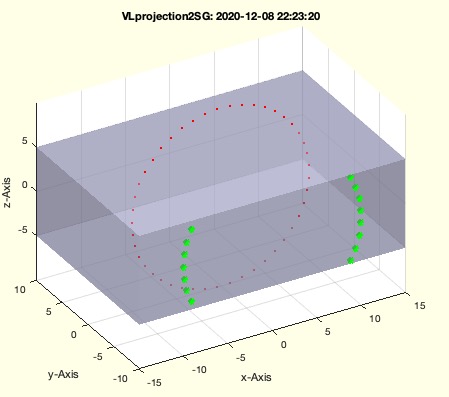
PL=PLcircle(10); VL=VLaddz(PL,0); VL=VL(:,[1 3 2]);
VLprojection2SG(SGbox,VL,[0 -1 0])
Copyright 2020-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function projects a vertex list (VL) onto a solid (SG) using a parallel projection defined by a normal vector (ez).
Input Parameters
- SG: The solid onto which the vertex list is projected. It contains vertex list (SG.VL) and face list (SG.FL).
- VL: The vertex list to be projected.
- ez: The normal vector defining the direction of the parallel projection.
Output
- VLN: The list of corresponding projection points. If no projection point exists, the result is NaN.
Algorithm Steps
- Initialize VLN as a NaN array with the same size as VL to store the projection results.
- Iterate over each vertex in VL:
- For each vertex, calculate the crosspoint using the function
crosspointVLFL with parameters SG.VL, SG.FL, the current vertex, and ez.
- If a crosspoint is found (i.e., it is not empty), store it in the corresponding position in VLN.
- If no output argument is specified (nargout == 0), visualize the results:
- Call
SGfigure to set up the figure with a specified range.
- Plot the solid SG using
SGplotalpha with white color and 0.5 transparency.
- Plot the original vertex list VL in red using
VLplot.
- Plot the projected vertex list VLN in green using
VLplot with a size of 2.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 00:14. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21