distE
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Analytical Geometry
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 1.0, Creation date: 2010-09-10, Last change: 2025-09-14
returns shortest distance to x/y plane and normal vector to p
Description
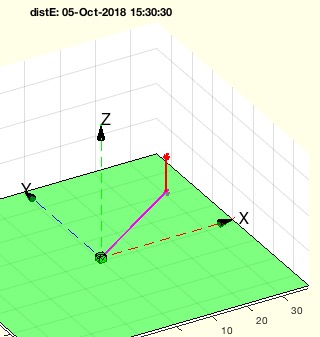
Shortest distance to x/y-plane is always the z value.
The normal vector is simply [0 0 z].
The orthogonal vector is p-n.
See Also: distT
, planedistanceofT
, VLisbelowT
Example Illustration
Syntax
[o,n]=distE(p)
Input Parameter
Output Parameter
o: | | orthogonal vector: 1x3 |
n: | | normal vector: 1x3 |
Examples
distE([30 20 10])
Copyright 2010-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, distE, calculates the shortest distance from a point to the x/y-plane and provides the normal and orthogonal vectors related to this point.
Input Parameters
- p: A vector of size 1x3 or 3x1 representing a point in 3D space.
Output Results
- o: The orthogonal vector, which is a 1x3 vector.
- n: The normal vector, which is a 1x3 vector.
Algorithm Steps
- Ensure the input vector
p is in the form [p(1) p(2) p(3)].
- Calculate the normal vector
n as [0 0 p(3)]. This vector is perpendicular to the x/y-plane.
- Compute the orthogonal vector
o as the difference between p and n, i.e., o = p - n.
- If no output arguments are specified, visualize the vectors and point using plotting functions:
- Set up a 3D figure with a specific view angle.
- Plot the transformation frame and vectors using
tfplot, tplot, VLplot, and lplot functions.
Example
To use the function, call it with a point, for example: distE([30 20 10]).
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-18 23:30. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21