SGhollowrhombus
by Tim C. Lueth, SG-Lib Toolbox: SolidGeometry 5.6 - Automatic Design
Introduced first in SolidGeometry 5.2, Creation date: 2022-06-19, Last change: 2025-09-15
creates a hollow soild for FDM printer
Description
It makes almost no sense since printing time and material use seem to be very similar (90%) even in case of small objects.
If the angle is larger than 50 degree most FDM printer can print hollow structures without support structures
See Also: , SGhollowsolid
Example Illustration
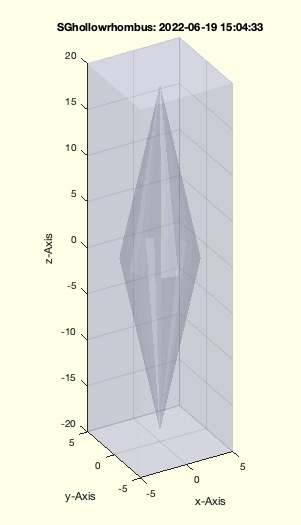
Syntax
SG=SGhollowrhombus(SG,[WNA]);
Input Parameter
SG: | | Solid Geometry |
WNA: | | [wall thickness, edge number, angle in degree]; default is [1.2 0 55] |
Output Parameter
SG: | | Solid with included rhombus to save material and printing time |
Examples
SGhollowrhombus(SGbox([10 10 40]))
SGhollowrhombus(SGsphere(30,'','','',30,60))
Copyright 2022-2025 Tim C. Lueth. All rights reserved. The code is the property of Tim C. Lueth and may not be redistributed or modified without explicit written permission. This software may be used free of charge for academic research and teaching purposes only. Commercial use, redistribution, modification, or reverse engineering is strictly prohibited. Access to source code is restricted and granted only under specific agreements. For licensing inquiries or commercial use, please contact: Tim C. Lueth
Algorithm (Workflow)
This function, SGhollowrhombus, is designed to create a hollow solid for FDM printers by incorporating a rhombus shape within the solid geometry. The purpose is to potentially save material and printing time, although the savings are minimal.
Input Parameters
- SG: The solid geometry object that will be modified.
- WNA: An optional parameter array consisting of:
- wall thickness: The thickness of the walls of the rhombus.
- edge number: The number of edges for the rhombus. If set to 0, it defaults to a circular shape.
- angle in degree: The angle of the rhombus in degrees, which is converted to radians within the function.
The default value for WNA is [1.2, 0, 55].
Algorithm Steps
- Retrieve the
WNA parameters using getfuncparams, with defaults if not provided.
- Convert the angle from degrees to radians.
- Determine if the edge number
n is zero. If so, set n and dd to empty arrays. Otherwise, calculate dd using dofn.
- Calculate the bounding box of the solid geometry using
sofBB.
- Project the solid geometry to a 2D plane and add auxiliary points using
CPLofSGprojection and CPLaddauxpoints.
- Calculate the minimum radius
rmin from the center point cp.
- Compute the dimensions
d and h for the rhombus.
- Calculate the rhombus angle
ra using atan2.
- Create a rhombus plane
PLR and convert it to a solid geometry SGR using SGofCPLrot.
- Check if the rhombus angle
ra is smaller than the specified angle a. If so, issue a warning. Otherwise, subtract the rhombus from the original solid geometry using SGsubtract.
- If no output is specified, write the result to an STL file and plot the geometry using
SGwriteSTL, SGfigure, and SGplotalpha.
Algorithm explaination created using ChatGPT on 2025-08-19 07:35. (Please note: No guarantee for the correctness of this explanation)
Last html export of this page out of FM database by TL: 2025-09-21